Introduction
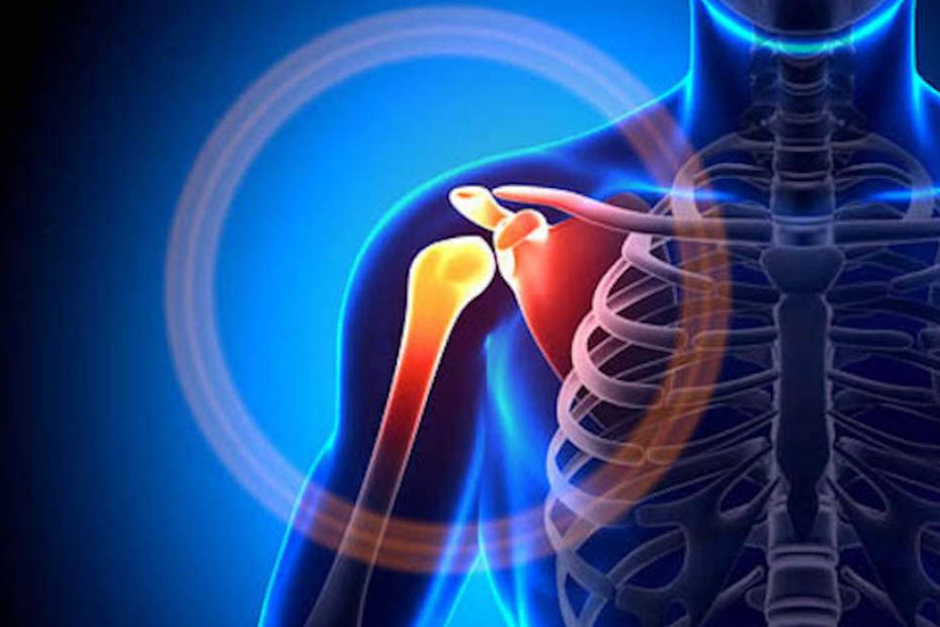
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a common condition that affects the shoulder joint, leading to pain and limited mobility. It occurs when the tendons or bursa in the shoulder become irritated or compressed, typically as a result of repetitive overhead movements. Women are particularly susceptible to shoulder impingement due to anatomical differences, hormonal factors, and certain activities or sports. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing symptoms and preventing further damage to the shoulder joint.
Overview
Shoulder impingement syndrome involves the narrowing of the space between the upper arm bone (humerus) and the shoulder blade (scapula), causing the tendons or bursa to become pinched. This condition can develop gradually, often due to repetitive motion or overuse, especially in activities like swimming, tennis, or weightlifting. Symptoms include pain when raising the arm, weakness, and limited range of motion. Proper diagnosis, followed by conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention, can help relieve pain and restore function.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Chronic Pain: If left untreated, shoulder impingement can lead to persistent pain, affecting daily activities and quality of life.
- Rotator Cuff Damage: Continued impingement may cause tendonitis or tears in the rotator cuff, leading to more severe shoulder dysfunction.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Long-term impingement can lead to stiffness, making it difficult to perform normal movements.
Understanding the Recovery Process
- Rest and Ice Therapy: Initially, rest and ice packs can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises improve shoulder mobility and relieve pressure on the affected tendons.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections can provide short-term relief to manage pain.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgery to remove damaged tissue or widen the shoulder space may be necessary.
Factors Influencing Outcomes
- Timeliness of Treatment: Early intervention with physical therapy can prevent the condition from worsening and lead to better outcomes.
- Severity of the Condition: Mild cases of impingement may resolve with conservative treatment, while severe cases may require surgery.
- Activity Level: Athletes or individuals with high physical demands may face longer recovery times or a need for more specialized rehabilitation.
- Age and General Health: Older women or those with other health conditions may experience slower healing times or complications.
Informed Decision-Making
- Choosing Treatment Options: Patients should discuss the benefits and risks of various treatments, including conservative options versus surgery.
- Understanding Rehabilitation: It is essential to commit to physical therapy and exercises to restore function and prevent future injuries.
- Post-Treatment Care: Following up with healthcare providers to monitor recovery and adjust treatment plans accordingly is important for long-term success.
Key Takeaway
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a treatable condition that requires early diagnosis and tailored treatment. Women can manage symptoms effectively through rest, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. In more severe cases, surgical options may be considered to prevent further damage and improve shoulder function.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance regarding shoulder pain or impingement syndrome.