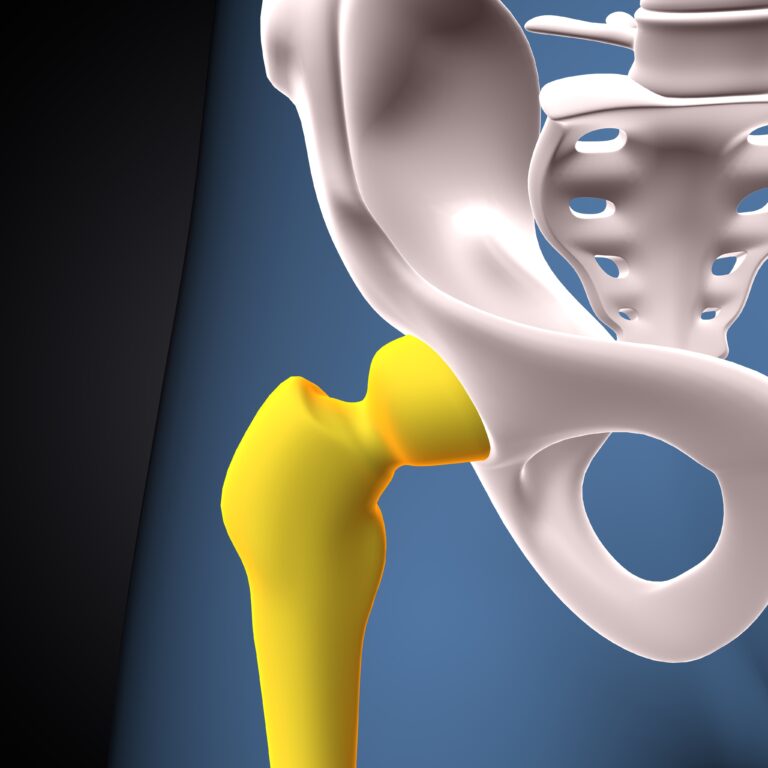
Hip pain can be a debilitating condition that significantly affects your daily activities and overall quality of life. This blog explores common causes of hip pain, specifically from injuries and arthritis, and introduces robotic-assisted surgery as an innovative treatment option.
What’s the Difference?
Causes of Hip Pain
1. Injuries
- Traumatic Injuries: Falls, sports injuries, and accidents can lead to hip fractures, dislocations, and soft tissue damage. These injuries can cause acute pain and long-term mobility issues.
- Overuse Injuries: Activities involving repetitive hip movements can result in conditions like tendinitis and bursitis, where inflammation of the tendons and bursae leads to pain and discomfort.
2. Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis: The most common form of arthritis affecting the hip, characterized by the gradual wearing down of the cartilage that cushions the hip joint. This leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder causing inflammation in the joints, including the hip. This leads to pain, swelling, and eventual joint damage.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops after an injury, such as a fracture or dislocation, can damage the cartilage and alter the mechanics of the hip joint.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: A form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine but can also cause hip pain and stiffness.
Symptoms of Hip Pain
- Groin Pain: Pain often radiates from the inside of the hip or groin.
- Pain on the Outside of the Hip: Often associated with bursitis or tendinitis.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the hip joint smoothly.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Inflammation of the hip joint or surrounding structures.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty with activities such as bending or rotating the hip.
Diagnosing Hip Pain
A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider typically involves:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: To assess symptoms and identify potential causes.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize the bones and soft tissues of the hip.
- Blood Tests: To check for markers of inflammation indicative of rheumatoid arthritis or other conditions.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is an advanced option for treating severe hip conditions. It offers several benefits over traditional surgical methods:
1. Precision: Robotic systems allow for highly accurate placement of implants and precise removal of damaged tissue. This precision can lead to better alignment and functioning of the hip joint.
2. Customized Planning: Preoperative planning software creates a 3D model of the patient’s hip, allowing surgeons to tailor the procedure to the individual’s anatomy.
3. Minimally Invasive: Robotic surgery often involves smaller incisions, which can reduce blood loss, minimize scarring, and shorten recovery time.
4. Enhanced Outcomes: The accuracy of robotic systems can lead to improved implant longevity and better overall outcomes for patients.
Conclusion
Hip pain from injuries and arthritis can significantly impact your life, but understanding the causes and available treatments can help you manage your condition effectively. Robotic-assisted surgery offers a promising option for those requiring surgical intervention, providing precision, customized care, and potentially better outcomes. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your specific needs.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice. Before making any health-related decisions, consult with a qualified healthcare professional. The content is not a substitute for medical advice, and individual results may vary. The author and website are not responsible for any consequences arising from the use of the information provided. Use your best judgment and seek professional advice when needed.