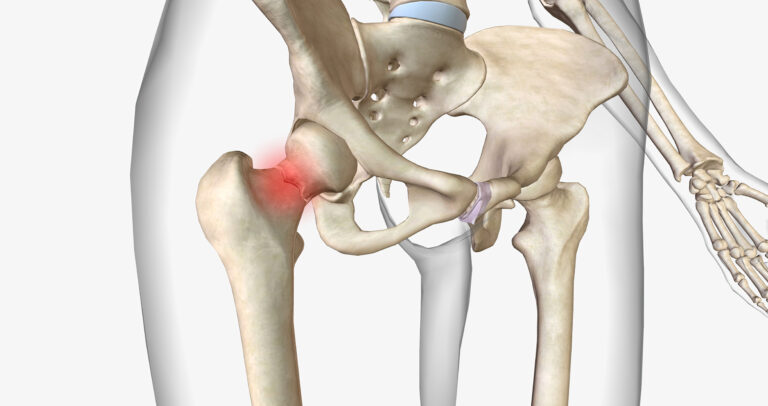
The hip joint is a fundamental part of our body’s mechanics, enabling a wide range of movements and bearing the weight of our upper body. Its complex structure and functions make it one of the most important joints in maintaining our mobility and quality of life. This blog will delve into the intricacies of the hip joint, its importance, common ailments, and tips for maintaining hip health.
The Anatomy of the Hip Joint
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the articulation between the femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum of the pelvis. This joint structure allows for significant flexibility and range of motion.
- Femoral Head: The rounded top part of the femur that fits into the acetabulum.
- Acetabulum: The cup-shaped socket in the pelvis that holds the femoral head.
- Articular Cartilage: This smooth, white tissue covers the surfaces of the femoral head and acetabulum, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement.
- Ligaments: Strong bands of tissue, including the iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments, which provide stability and limit excessive movement.
- Muscles and Tendons: The hip joint is surrounded by powerful muscles, such as the gluteals, hip flexors, and adductors, which facilitate movement and provide additional stability.
Common Hip Joint Issues
Despite its robust design, the hip joint is susceptible to various issues, including:
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint disease results from the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the joint lining, resulting in pain and swelling.
- Hip Fractures: Common in older adults, these fractures often occur due to falls and can significantly impact mobility.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, the small sacs of fluid that cushion the hip joint, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Labral Tears: Tears in the ring of cartilage (labrum) surrounding the acetabulum can cause pain and clicking sensations in the hip.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the hip, often due to overuse, can cause pain and limited movement.
Maintaining Hip Health
To keep your hips healthy and functional, it’s important to adopt preventive measures and healthy habits. Here are some tips:
1. Exercise Regularly
Engage in activities that strengthen the muscles around the hip joint. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking are great options. Incorporate strength training exercises, like squats and lunges, to build muscle around the hips.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying excess weight can put additional strain on the hip joint. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce this stress.
3. Practice Good Posture
Good posture can prevent unnecessary strain on the hip joint. Be mindful of your posture while sitting, standing, and moving. Use ergonomic furniture and consider practices like yoga or Pilates to improve your posture and alignment.
4. Stretch and Strengthen
Incorporate stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine. Focus on the muscles around the hips, such as the glutes, hip flexors, and adductors. Regular stretching can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injuries.
5. Use Proper Techniques
When lifting heavy objects or engaging in activities that involve repetitive movements, use proper techniques to avoid putting undue stress on your hips. Bend at your knees, not your waist, and use your leg muscles to lift.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you experience persistent hip pain or suspect a hip injury, it’s important to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further damage and improve your quality of life. Treatment options may include physical therapy, medications, or, in severe cases, surgery.
Conclusion
The hip joint is essential for our everyday movements and overall mobility. By understanding its structure and function, and by adopting healthy habits, we can keep our hips strong and flexible. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and using proper techniques can go a long way in preventing hip problems and ensuring a healthy, active lifestyle.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice. Before making any health-related decisions, consult with a qualified healthcare professional. The content is not a substitute for medical advice, and individual results may vary. The author and website are not responsible for any consequences arising from the use of the information provided. Use your best judgment and seek professional advice when needed.