Introduction:
Hip dysplasia, a condition where the hip socket doesn’t fully cover the ball of the thighbone, disproportionately affects women, often leading to arthritis if untreated. This blog covers the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for hip dysplasia, focusing on how early diagnosis and surgical interventions can help preserve joint function.
Understanding Hip Dysplasia:
- Developmental Causes: Hip dysplasia often develops from birth due to improper formation of the hip socket.
- Genetic Factors: Women with a family history of hip dysplasia are more likely to develop the condition.
- Athletic Influence: High-impact sports like gymnastics and running can worsen undiagnosed hip dysplasia over time.
Symptoms of Hip Dysplasia in Women:
- Hip Pain: Discomfort or sharp pain in the groin area during physical activity.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty in moving the leg outward or performing activities that require hip flexibility.
- Limping: An abnormal walking gait caused by instability in the hip joint.
Treatment Options for Hip Dysplasia:
- Non-Surgical Treatments: Physical therapy and pain management for mild cases.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO): A procedure to reorient the hip socket to provide better coverage for the ball of the hip.
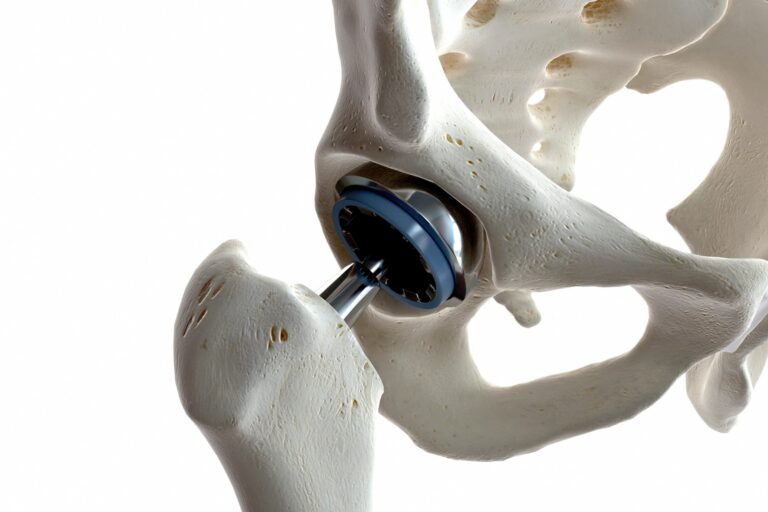
- Hip Replacement: In severe cases of arthritis or damage, a total hip replacement may be necessary.
- Rehabilitation Post-Surgery: Recovery requires physical therapy to restore movement and strength in the hip joint.
Long-Term Impact of Hip Dysplasia:
Without treatment, hip dysplasia can lead to early-onset arthritis and chronic pain, significantly impacting a woman’s quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are critical for maintaining hip function and preventing complications later in life.
Disclaimer:
The information provided is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan for hip dysplasia. The causes, symptoms, and surgical options may vary based on individual health conditions. This content aims to raise awareness and guide women in understanding hip dysplasia and its management. Results from surgical interventions can differ depending on the severity of the condition and individual response to treatment.