Introduction
Orthopedic pain is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide, often leading to decreased mobility, functionality, and quality of life. Whether caused by arthritis, injury, or chronic conditions, effective management is crucial to helping individuals recover, maintain mobility, and improve their overall well-being. A multi-faceted approach that incorporates medication, physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and advanced treatments can significantly enhance pain relief and healing.
Overview
Orthopedic pain management is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It requires a personalized strategy that addresses the underlying causes of pain while promoting recovery and preventing long-term damage. Modern orthopedic pain management emphasizes a combination of traditional methods and advanced treatments, focusing on both immediate relief and long-term outcomes. This approach allows patients to regain function, reduce discomfort, and improve their quality of life.
Effective Pain Management Strategies
- Medications:
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These are often used to reduce inflammation and relieve mild to moderate pain associated with conditions like arthritis or soft tissue injuries.
- Acetaminophen: An effective option for those who cannot tolerate NSAIDs, particularly for managing mild to moderate pain.
- Opioids: Reserved for severe pain, opioids can be effective but are generally used short-term due to the risk of dependence and side effects.
- Corticosteroids: These drugs reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, often used in joint injections for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Physical Therapy:
- Exercise and Stretching: A structured exercise program strengthens muscles, supports joints, and improves flexibility, which can relieve pain and prevent future injury.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques like joint mobilization, soft tissue manipulation, and massage therapy can alleviate pain and improve movement.
- Heat/Cold Therapy: Alternating between hot and cold compresses can help reduce swelling, improve blood circulation, and ease muscle tension.
- Interventional Pain Management:
- Joint Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections are commonly used to treat inflammation or degenerative joint conditions, offering significant pain relief.
- Nerve Blocks: These injections help block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing targeted relief for conditions like sciatica or nerve compression.
- Spinal Cord Stimulation: A device is implanted to send electrical pulses to the spinal cord, interrupting pain signals and offering relief for chronic pain.
- Surgical Options:
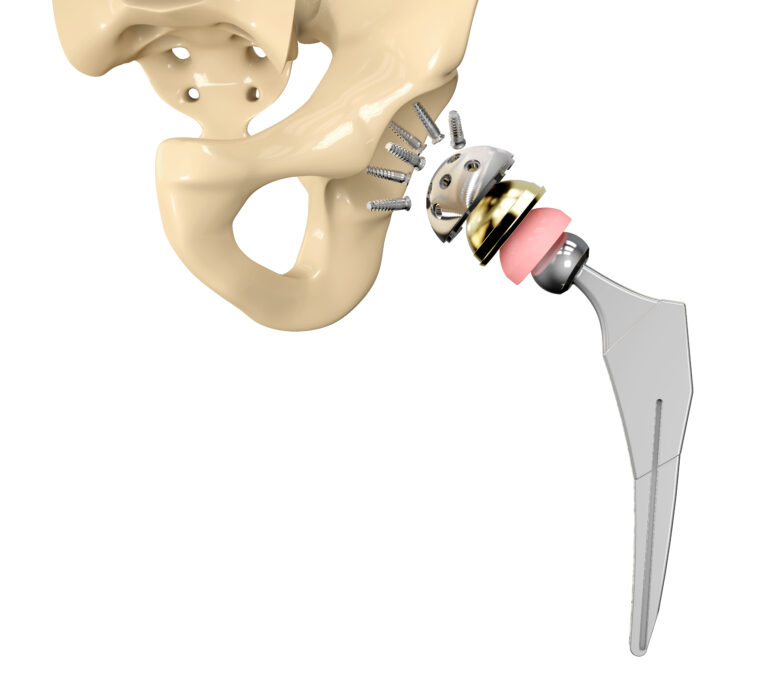
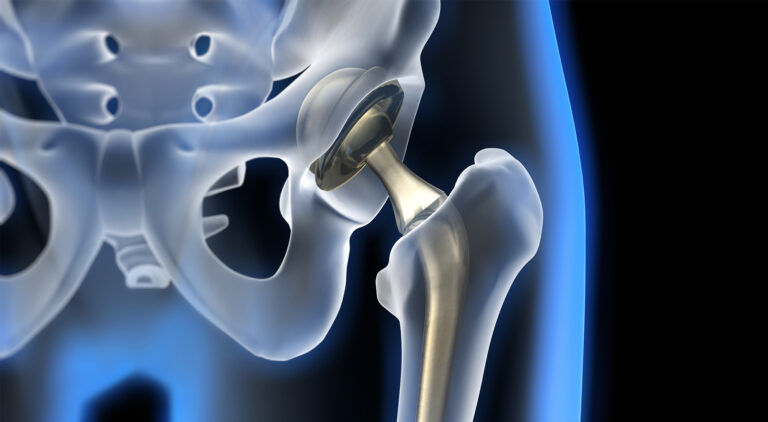
- Joint Replacement: When conservative treatments fail, surgeries like hip or knee replacement may be necessary to restore joint function and alleviate pain.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure used to repair cartilage or remove damaged tissue from joints, reducing pain and improving joint function.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Medication Side Effects:
Long-term use of pain medications, especially opioids, can lead to dependency, gastrointestinal problems, and liver or kidney damage. - Surgical Risks:
Any surgical procedure carries inherent risks, such as infection, blood clots, or complications related to anesthesia. Additionally, there may be a risk that the surgery does not fully relieve pain or restore function. - Injection Complications:
Invasive treatments like joint injections or nerve blocks can lead to side effects like infection, bleeding, or allergic reactions. Overuse of certain injections may also cause joint deterioration over time.
Understanding the Recovery Process
Recovery from orthopedic pain management strategies varies depending on the method used. Medications and physical therapy generally offer quicker relief, while surgical treatments may require longer recovery periods, involving physical therapy and gradual return to activity. Patients must follow their treatment plan closely, which often includes rest, rehabilitation, and activity modification toensure optimal recovery.
Key Takeaway
Managing orthopedic pain effectively requires a personalized, comprehensive approach that combines medications, physical therapy, interventional treatments, and surgery. By addressing both immediate pain and long-term recovery, patients can regain mobility, enhance quality of life, and reduce the risk of chronic pain.
Disclaimer
This overview is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment for your individual condition.